
Cycloidal Gearboxes
Cycloidal gearboxes are a specialized type of gear system characterized by their distinctive design and operational principles. Unlike traditional gear mechanisms, cycloidal gearboxes utilize a cycloidal disk that moves in a cycloidal motion to transfer motion and power.
This unique approach to power transmission offers several advantages, including high precision, low backlash, and the ability to withstand high loads, making them particularly suitable for applications requiring precise control and durability.
Cycloidal Gear Box Options From Sumitomo
The Fine Cyclo® product series is a high-precision cycloidal gearbox with zero backlash. These single- and double-stage cycloidal drives are highly compact in design, provide long life, and can be optimally integrated into your application. Their high torsion, combined with their low moments of inertia, create ideal solutions for highly dynamic tasks.

Torque
Nominal: Up to 12,000 N•m (106,209 lb•in) / Acceleration: Up to 30,000 N•m (265,522 lb•in)

Diameter
Up to 138 mm (Hollow Bore)

Ratio Range
29:1 to 283:1

Input Speed
Up to 10,260 RPM
Fine Cyclo DA-Series
High precision gearbox with highest torque density in a single-stage
Angular contact ball bearings are directly integrated into the gearbox housing.
Improved design providing very accurate motion quality and increased torque density and bearing capacity.
- Highest torque density in a single-stage unit
- Ideal for robotic applications
- Hollow shaft possible
- Fully sealed modular version with motor adapter and clamp ring available
Fine Cyclo UA-Series
Highly efficient traverse movement. Two-stage cycloidal gearbox with a planetary 1st stage and cycloidal 2nd stage.

Fine Cyclo C-Series
High-precision cycloidal drive with a large hollow bore and a high-capacity bearing directly integrated into the gearbox housing.

Fine Cyclo T-Series
Spur gear two-stage high-precision cycloidial gear box. It comes pre-staged and has three eccentrics.

Fine Cyclo W-Series
High-load precision one-stage cycloidal gearbox with extremely large hollow shaft and integrated pre-stage.

Fine Cyclo A-Series
A-Series FC Type
Cost-effective high-precision cycloidal gear reduction kit without an output bearing

A-Series F1 Type
Combination of zero backlash cycloidal gearbox and precision cross roller bearing.

A-Series F2 Type
All-rounder cycloidal gear box with a compact housing. Suitable for all automation tasks.

A-Series F3 Type
High-precision cycloidal gearbox providing a high radial capacity at the solid output shaft.

Discover Precision Engineering with Our Motion Control Products Brochure
Explore our detailed brochure to understand the range and capabilities of our motion control solutions.
Our gearboxes, designed for precision and durability, cater to various industrial requirements, offering zero backlash, high torque capacities, and exceptional performance.
The brochure covers our product lineup, including our cycloidal gearbox line, harmonic drive/strain wave gearbox line, and servo gearbox options.
More Information About Cycloidal Gearboxes
Explore the distinctions between single-stage and multi-stage cycloidal gear boxes and their applications.

Discover the key differences between these gearboxes and Harmonic Drive Gearboxes to select the perfect drive solution for your robotics application.

Here is a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about cycloidal drives and their answers.

Download our Zero Backlash Precision Drive catalog for all the technical specs you need to build the perfect cycloidal gearbox for your operation.
Top Features of a Cycloidal Drive
-
High Reduction Ratios: Cycloidal gearboxes are capable of providing very high reduction ratios in a single stage, often ranging from 30:1 to over 100:1, and even higher in multi-stage configurations. This is significantly higher than what is typically achievable with other types of gearboxes in a single stage, making them ideal for applications requiring substantial speed reduction and torque amplification.
-
Compact Design: Despite these high reduction ratios, cycloidal gearboxes maintain a compact and efficient design. This is due to the efficient transmission of force through the cycloidal discs and the reduction mechanism's inherent stability and balance.
-
Precision and Low Backlash: The gear ratio, combined with the operational characteristics of the cycloidal motion, results in very low backlash. This makes cycloidal drives suitable for applications requiring high precision and repeatability, such as robotics, machine tools, and automation systems.
-
Durability and Load Capacity: The cycloidal design evenly distributes loads across multiple contact points between the cycloidal disc and the pins. This distribution, along with the gearbox's inherent mechanical advantage, enhances its durability and ability to withstand high loads.
Understanding Gear Ratio in Cycloidal Gear Boxes
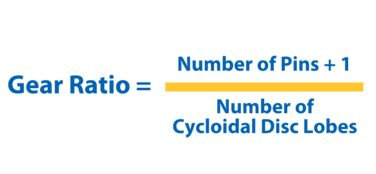
The gear ratio of a cycloidal gearbox is the ratio between the input speed (rotations of the input shaft) and the output speed (rotations of the output shaft). It indicates how many times the input shaft must turn to achieve one full rotation of the output shaft.
In cycloidal gearboxes, the gear ratio is determined by the number of lobes on the cycloidal disc and the number of pins (or teeth) engaging with the disc, plus one. This formula reflects the unique way that they transfer motion, with the gear ratio being adjustable by changing the number of lobes on the cycloidal disc or the number of pins it interacts with.
Selection Criteria for Applications
Here are the most common selection criteria for selecting a unit from top Cycloidal gearbox manufacturers such as Sumitomo Drive Technologies.
| Selection Criteria | Importance | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction Ratio | High | Essential for determining the output speed based on the required application. |
| Torque Capacity | High | Must match or exceed the maximum load the application will impose. |
| Backlash | Medium to High | Critical for applications requiring high precision. |
| Size and Weight | Medium | Important for applications with limited space. |
| Efficiency | Medium | Higher efficiency may be necessary for energy-sensitive applications. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here is a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about these cycloidal gearbox applications, cycloidal gearbox assembly, and more.
What is a cycloidal gearbox, and how does it operate?
What is a cycloidal gearbox, and how does it operate?
A cycloidal gearbox or cycloidal drive is a type of mechanical gearbox designed for high precision and torque transmission efficiency with minimal backlash. It operates on the principle of a cycloidal disc moving in an eccentric path, engaging with pins on the gearbox housing to convert input rotation into a reduced output rotation.
What are the main advantages of using a cycloidal gearbox?
Cycloidal gearboxes offer several advantages, including high reduction ratios, compact design, exceptional load-bearing capacity, minimal backlash, and excellent shock resistance. These features make them ideal for applications requiring precise motion control and reliability under heavy loads.
How do single-stage and multi-stage gearboxes differ?
Single-stage cycloidal gearboxes provide reduction in one step, making them compact and efficient for applications requiring moderate reduction ratios. Multi-stage drives, on the other hand, offer higher reduction ratios by employing multiple cycloidal discs and pin sets in series, catering to applications needing extreme precision and torque.
Learn more about their differences in this blog:
What is input rotational speed?
What is Input Rotational Speed?
Input rotational speed is the speed at which the gearbox's input shaft is driven, usually by an electric motor. It’s the initial speed that will be reduced according to the gearbox's reduction ratio to achieve the desired output speed.
Can Sumitomo motion control products be customized for specific applications?
Can Sumitomo motion control products be customized for specific applications?
Yes, Sumitomo cycloidal gearboxes can be customized to meet specific requirements, including size, torque capacity, reduction ratios, and mounting configurations. This adaptability allows them to be tailored to a wide range of industrial applications.
How do I choose the right cycloidal gearbox for my application?
Choosing the right cycloidal gearbox involves considering several factors, including the required torque, reduction ratio, space constraints, load capacity, and environmental conditions.
What Is the output torque of a cycloidal gearbox and how is it calculated?
What Is the output torque of a cycloidal gearbox and how is it calculated?
The output torque of a cycloidal gearbox measures the rotational force available at the gearbox's output shaft. It's a critical parameter for users who need to ensure that their mechanical system has enough force to perform its intended tasks. Their unique design allows them to deliver high-output torque from a compact form factor, making them especially valuable in applications requiring high power in limited spaces.
How does backlash in these gearboxes compare to other gearbox types?
How does backlash in these gearboxes compare to other gearbox types?
Cycloidal gearboxes are designed to achieve extremely low backlash compared to other gearbox types. This makes them ideal for precision applications where accurate positioning and motion control are critical.
What makes cycloidal gearboxes highly efficient in power transmission?
What makes cycloidal gear boxes highly efficient in power transmission?
This drive type achieves high efficiency in power transmission due to its unique design, which minimizes slippage and energy loss. The direct contact between the cycloidal disc and the pins ensures that energy is transmitted effectively, leading to efficiencies typically above 90% for these systems.
How do the gears in a cycloidal gearbox differ from traditional gears?
How do the gears in a cycloidal gearbox differ from traditional gears?
Cycloidal gearboxes feature a unique design that fundamentally differs from traditional gear systems. Instead of using standard gears with teeth that mesh together, a cycloidal gearbox utilizes a cycloidal disc that interacts with a series of pins or rollers. This design provides several operational advantages over conventional gears
Key Differences:
-
Cycloidal Discs vs. Gear Teeth: In a cycloidal gearbox, the primary motion-transmitting component is the cycloidal disc, which moves in a cycloidal path, engaging with fixed pins or rollers in the gearbox housing. This contrasts with traditional gears, where motion is transmitted through the direct engagement of teeth on mating gears.
-
Transmission Method: The cycloidal disc in a cycloidal gearbox generates motion through an eccentric, rather than rotational, movement. This eccentric movement is converted into the desired rotational output through the engagement of the disc's lobes with the external pins or rollers. In contrast, traditional gear systems rely on the direct rotational interaction of gear teeth.
-
Load Distribution: The load in a cycloidal gearbox is distributed over a larger area due to the engagement between the cycloidal disc's entire lobe surface and the pins or rollers. Traditional gears transmit force at the contact points between individual teeth, which can lead to increased wear and localized stress.
What role do rollers and pins play?
What role do rollers and pins play, and how do they contribute to the gearbox's performance?
A: Rollers and pins are critical gear drive components, contributing significantly to their efficiency, durability, and precision. These elements work together to transmit power from the input shaft to the output shaft with minimal backlash and high torque capacity.
Role and Function:
-
Pins: Fixed in the gearbox housing, the pins serve as the contact points for the cycloidal disc. As the input shaft turns the eccentric cam, it causes the cycloidal disc to move in a unique, cycloidal path. The motion of the cycloidal disc is then translated into rotation of the output shaft through its interaction with these pins.
-
Rollers: Attached to the cycloidal disc, rollers fit between the fixed pins. They ensure smooth, efficient transfer of motion from the cycloidal disc to the output shaft. The rollers reduce friction and wear at the contact points between the cycloidal disc and the pins, enhancing the gearbox's longevity and maintaining its precision over time.
Contribution to Performance:
-
High Torque Transmission: The interaction between the cycloidal disc's rollers and the fixed pins allows the drive to transmit high levels of torque efficiently. This is due to the large contact area between the rollers and pins, which distributes forces more evenly and allows for the transmission of higher loads without significant wear.
-
Minimal Backlash: One of the key advantages is their ability to operate with minimal backlash. The precise fit and continuous engagement between the rollers and pins eliminate play in the transmission path, resulting in superior accuracy and repeatability in motion control applications.
-
Durability and Reliability: The use of rollers reduces point contact stress and distributes loads over a larger area, minimizing wear and extending the service life of the gearbox. This makes the drive exceptionally durable and reliable, even in applications involving high loads or continuous operation.
What are cycloidal gears, and how do they work?
What are cycloidal gears, and how do they work?
Cycloidal gears are a type of gear mechanism that is distinct from traditional spur or helical gears. Unlike conventional gears, which transmit torque through the meshing of teeth, cycloidal gears operate using a cycloidal disc that moves in a complex, cycloidal path. This movement engages with pins or rollers positioned around the gear housing, converting input rotational motion into reduced output rotational motion with high torque and minimal backlash.
Are cycloidal discs and cycloidal gears the same thing, or is there a difference between them?
Are cycloidal discs and cycloidal gears the same thing, or is there a difference between them?
The terms "cycloidal discs" and "cycloidal gears" are closely related and often used within the context of cycloidal gearboxes, but they refer to different components of the system.
-
Cycloidal Discs: These are the heart of a cycloidal drive system. A cycloidal disc is a specialized component that features a series of lobes or curves around its perimeter. The disc moves in a cycloidal motion (a complex path that combines circular and linear motion) as it is driven by an eccentric bearing attached to the gearbox's input shaft. This motion allows the cycloidal disc to engage with pins or rollers fixed in the gearbox housing, thereby converting the input rotational motion into output rotational motion with a significant reduction in speed and an increase in torque.
-
Cycloidal Gears: This term can be somewhat misleading because it suggests traditional gear mechanisms. However, in the context of a cycloidal drive system, "cycloidal gears" refers to the overall mechanism that includes the cycloidal discs, along with the pins or rollers they interact with, and other associated components such as the input shaft, eccentric cam, and output shaft. Essentially, "cycloidal gears" encompass the entire drive system that utilizes cycloidal motion for power transmission.
Why is the input shaft of a Cycloidal gear box important?
Why is the input shaft of a Cycloidal gear box important?
The input shaft of a cycloidal gearbox plays a crucial role in the operation of the gearbox, acting as the primary interface for transmitting rotational power from the motor or driving mechanism to the gearbox itself.
How does the input shaft engage with the Eccentric Cam?
How does the input shaft engage with the Eccentric Cam?
In a cycloidal gearbox, the input shaft typically drives an eccentric bearing or cam that is directly attached to, or integrated with the cycloidal disc. The eccentric rotation of this cam, driven by the input shaft, causes the cycloidal disc to follow a cycloidal path, leading to the unique motion that characterizes this type of gearbox.
How do reduction gear ratios affect output rotational speed?
How do reduction gear ratios affect output rotational speed?
The reduction ratio of a cycloidal gearbox directly determines the output rotational speed. This ratio represents the difference between the input and output speeds and is a fundamental characteristic of the gearbox design. They can achieve very high reduction ratios in a compact form factor, significantly reducing the output speed while increasing torque.
What factors influence Rotational Speed?
What factors influence Rotational Speed?
-
Design and Configuration: The specific design of the cycloidal discs, the number of lobes, and the arrangement of the eccentric cam and roller pins all influence the achievable reduction ratios and, consequently, the output rotational speed.
-
Load Conditions: Under heavy load conditions, the actual output speed might slightly differ from the theoretical value due to mechanical losses within the gearbox. Cycloidal drives, however, are known for their efficiency and ability to maintain consistent output speeds even under varying load conditions.
-
Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication and maintenance are essential to ensure that the cycloidal gearbox operates at its optimal rotational speed. Friction and wear can affect performance over time, but the cycloidal design's inherent durability minimizes these effects.
How does the addition of stages impact a cycloidal gear box's performance in an application?
How does the addition of stages impact a cycloidal gear box's performance in an application?
To achieve even higher reduction ratios or to customize the gearbox for specific torque requirements, cycloidal gearboxes can be designed with multiple stages. Each stage adds to the overall reduction ratio by compounding the effect of the previous stage. This "addition" of stages allows for an extensive range of reduction ratios and flexibility in designing systems that require very low output speeds and high torque from a relatively high-speed input.
What Are the Disadvantages of a Cycloidal Gearbox?
What Are the Disadvantages of a Cycloidal Gearbox?
Cycloidal gearboxes offer several advantages, but they also have a few potential disadvantages to consider:
- Complex Assembly: The internal mechanism involves precision components that may require careful handling and assembly.
- Higher Initial Cost: Compared to traditional gearboxes, cycloidal drives can be more expensive due to their specialized design and materials.
- Vibration Sensitivity: Some models may experience increased vibration during operation if not properly aligned or if the pins and rollers wear out.
- Backlash in Lower-Quality Units: Poorly manufactured cycloidal gearboxes may introduce more backlash, which can affect precision in certain applications.
Why Is a Cycloidal Gear Not Used in All Applications?
Why Is a Cycloidal Gear Not Used in All Applications?
Cycloidal gears are not used in all applications due to:
- Application-Specific Design: Cycloidal gearboxes excel in applications requiring high torque and shock load resistance but may not be suitable for high-speed or lightweight applications.
- Precision Needs: For high-speed or extremely precise rotational tasks (e.g., robotics arms with minimal error tolerance), planetary or harmonic drives may be preferred over cycloidal designs.
- Size Constraints: Cycloidal gearboxes tend to be bulkier than some other types of gearboxes, making them less ideal for space-constrained environments.

Ready to Design Your Zero Backlash Gearbox?
Cycloidal Gearbox design is simple. with our online Product Configurator. This tool streamlines the selection process, enabling you to build a best motion control product for your specific application. Choose Sumitomo as your go-to Cycloidal Gearbox manufacturer.